How to Calculate Combustion Air
Note: This calculation is not required for sealed combustion/direct vent
Nowadays, the amount of air for combustion is pretty limited because we're trying to cut down on fuel use. We're replacing our windows, doors, weatherstripping, caulking, and adding insulation. When I first started in this field, there were no double-pane windows in basements, let alone steel-insulated doors leading outside. Instead, there were just old single-pane glass windows and wooden doors that often had gaps where light could come through the frame.
These days, we've got thermopane windows in the basements and new steel doors with magnetic seals. We even insulate the area between the floor joists on the outside. While all these upgrades are significant, they ultimately reduce the combustion air that's crucial for a safe burning process. If your heating system pulls air from inside your home for combustion, monitor the amount of air needed to ensure safety.
Examine this image of a residence. I assert that all heating devices should have combustion air supplied directly to them. You might be curious about the reason for this. When the air within the home is utilized for combustion, it decreases the pressure inside the house. This reduction in pressure causes cold air to be drawn in through any gaps and openings, which can lower the home's temperature and necessitate heating recovery. Supplying outdoor air to the appliance can prevent this issue. Insufficient combustion air may lead the appliance to draw air down the chimney, which can result in the intake of combustion byproducts, including carbon monoxide (CO).
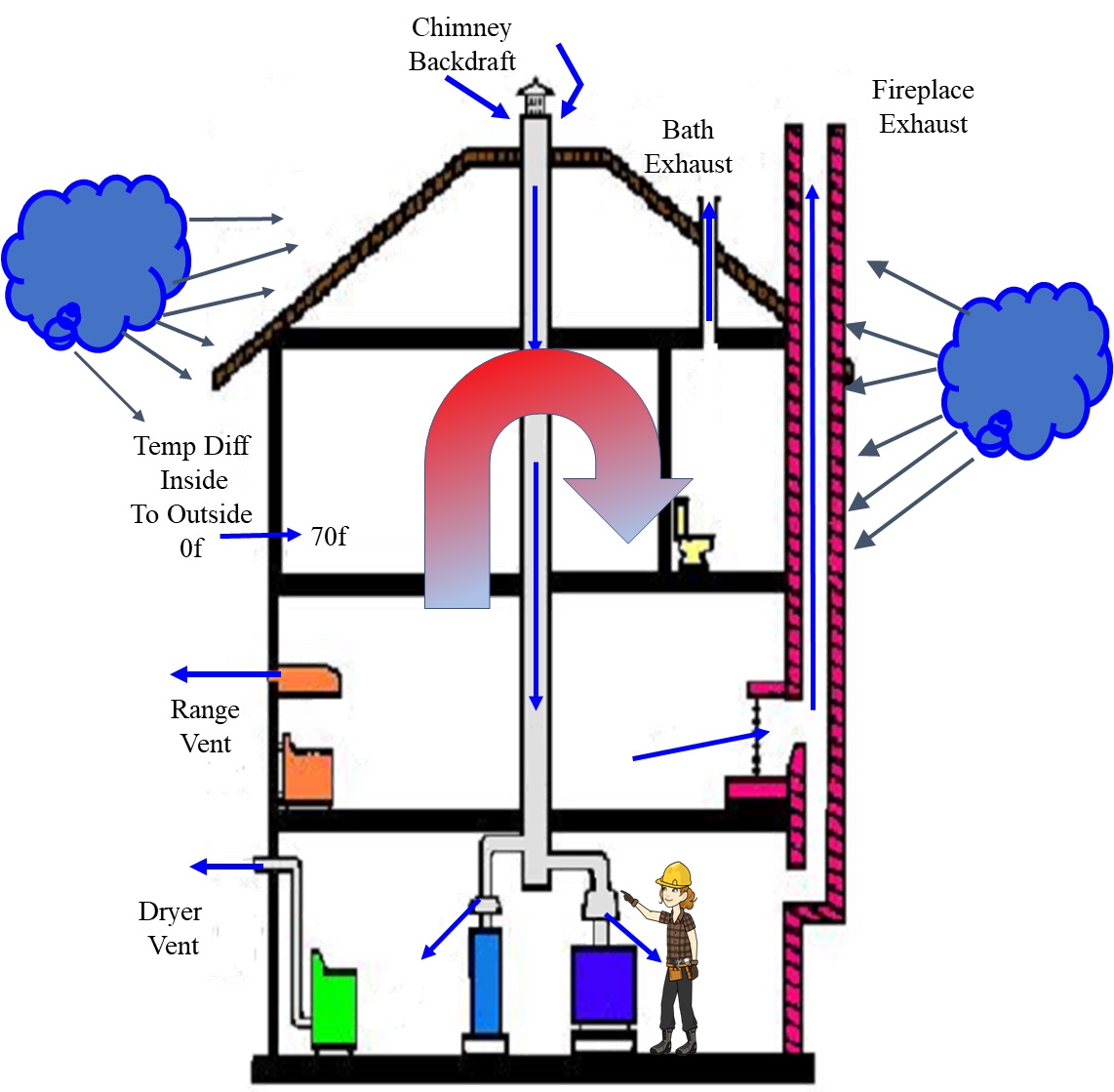
A residence can lose combustion air through kitchen and bathroom exhaust fans, clothes dryer vents, and woodstoves or fireplaces that lack an outdoor air connection, which can diminish the oxygen levels within the home. Additionally, outdoor air temperature influences the availability of combustion air; as outside temperatures drop, the structure experiences greater heat loss. It is important to note that heat loss refers to air escaping from the home. Furthermore, the height of the building can enhance thermal circulation, leading to increased heat loss.
The combustion process necessitates that the air used contains 20.9% oxygen. If the oxygen level is lower, the flame will begin to generate excess carbon monoxide (CO), an odorless gas that can be inhaled, hindering the body's ability to absorb oxygen. Each year, CO poisoning results in fatalities in the USA. It is essential to be increasingly vigilant about this issue as we enhance the insulation of our homes and utilize appliances that rely on indoor air for combustion.
Below is a chart that shows concentration values and the adverse effects of CO in the air.
Even a small amount of CO can become problematic. When considering this in terms of parts per million, it is quite striking. Let us examine the required air volume. The federal regulations stipulate that there should be 50 cubic feet of space for every 1,000 BTUs of input from your heating appliance. Local or state codes may have stricter requirements. By determining the input of the appliance and dividing it by the total cubic feet of the mechanical room, the result must be at least 50 cubic feet per 1,000 BTUs. If the space does not meet this requirement, it is necessary to introduce combustion air from outside. Additionally, if there are hallways or other rooms connected to the mechanical room without a door, we can factor in these areas as well.
It is important to assess all potential sources of combustion air until reaching a doorway with a door. The regulations specify that even if the door is louvered, calculations should cease at the point where the door meets the wall. If the utility room has a door, even if it remains open, we stop at that point. The formula utilizes BTUs in MBH (thousand BTUs per hour), meaning the last three zeros are omitted. For instance, 130,000 BTUs would be represented as 130. Now, let us consider a mechanical room that includes a door.
If we did the math it would look like this;
32 feet long x 25 feet wide x 7 feet high
Boiler = 130,000 Btuh input and a 40,000 Btuh Water Heater
Volume = Length x Width x Height
' Volume = 32' x 25' x 7' = 5600 Cubic Feet
Total Btuh Input = 130 MBH + 40 MBH = 170 MBH
5600 Cubic Feet / 170 MBH = 32.95 Cubic Feet per 1000 BTU
Combustion Air will be Required
Direct communication with outdoors (grille through wall) - 1 sq in per 4000 BTUs input
*Vertical duct - 1 sq in free area per 4000 BTUs input
*Horizontal duct - 1 sq in per 2000 BTU input
*Cross section of duct must equal opening free area
If you want to use a round duct, this chart will give you square inches of round duct.
Let's look at an actual job site I was on and how it was calculated.
Boiler 130,000 btu/h
Water Heater 45,000 btu/h
15 x 15 x 7 = 1575 cu ft
Appliances 130 + 45 = 175 mbh
1575 cu.ft. / 175 mbh = 9 cu.ft. per 1000 BTUs (should be a minimum of 50)
9 cu. Ft. / 50 cu. ft. required = 18% of required
175,000 /4000* = 43.75 free sq. in. needed
43.75 x 0.82 = 35.87 free sq. in.
* Direct communication with the exterior of the home
Some states have increased the 50 cubic feet per 100 BTUs per 1000 BTUs. This is a safer number because homes are more airtight today, and the air required for combustion will enter more slowly. You can change the cu. Ft. per thousand BTUs in your formulas if you have tightened up the home, or the home was built since 1970.
Here is the same formula above using 100 cu. in. per thousand btu's
|
Applications |
BTU's Per Square Inch |
|
Direct Communication to Outside (Grilles) |
4000 BTUs per 1 sq. in. |
|
Vertical Duct |
4000 BTUs per 1 sq. in. |
|
Horizontal Duct |
2000 BTUs per 1 sq. in. |
|
Grilles to interior rooms |
1000 btu's per 1 sq. in. |
